Intravascular Lithotripsy Holds Promise 2:1 Versus Absorbable Stents In PAD
Vascular surgeons and interventional radiologists, showed twice the level of enthusiasm for the innovation offered by Intravascular Lithotripsy than the next technology believed to show most promise, absorbable stents, in offering innovation in Peripheral Arterial Disease PAD treatment over the next three years.
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE.
Vascular surgeons and interventional radiologists, show twice the level of enthusiasm for the opportunities offered by Intravascular Lithotripsy (IVL) than the next technology believed to show most promise, absorbable stents, in offering innovation in Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) treatment over the next three years.
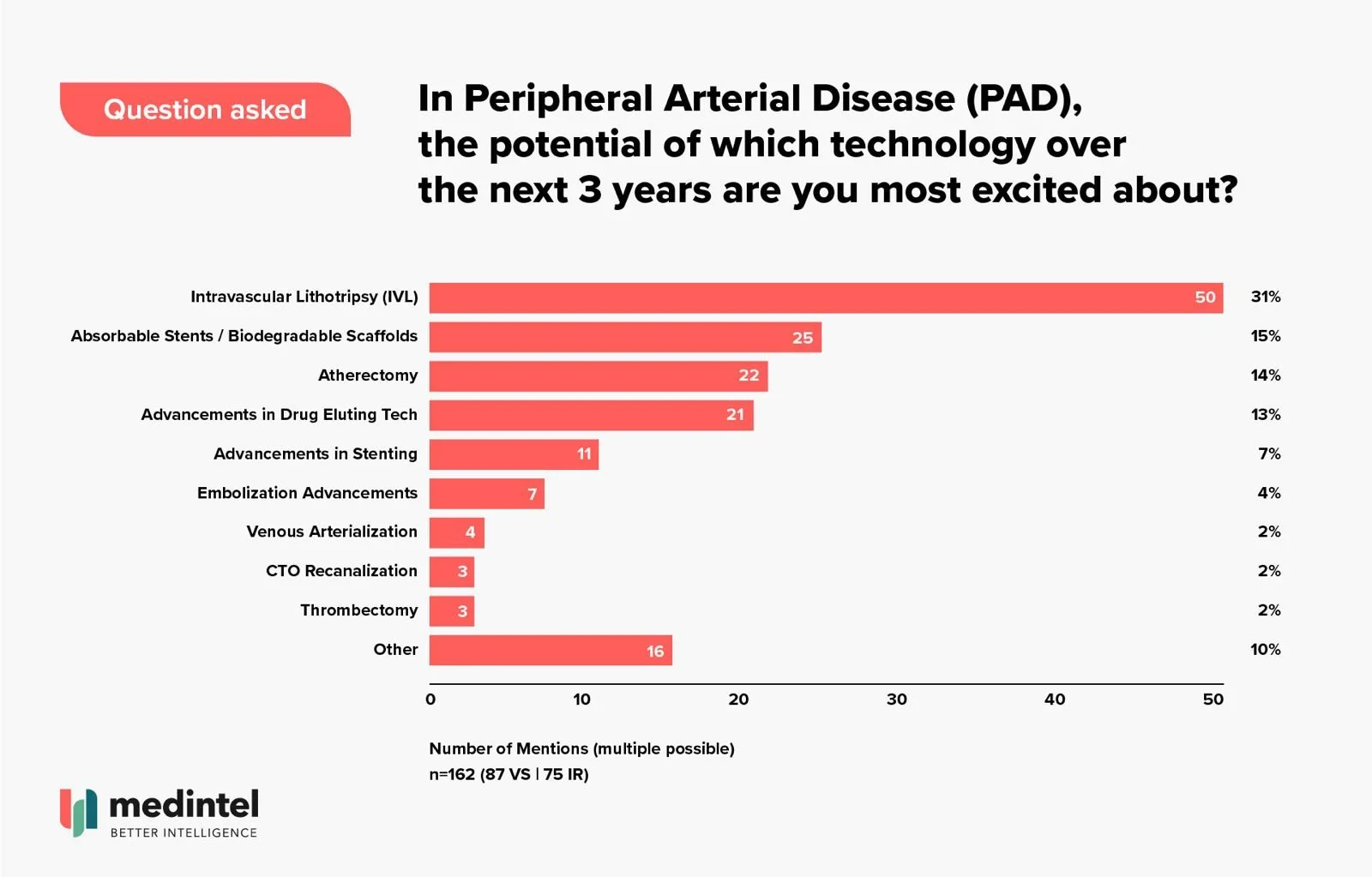
medintel surveyed 162 physicians (interventional radiologists, vascular surgeons) from across the EU and US, and 31% of physicians named IVL as the technology they're most excited about over the next three years.
This represents more than double the interest in the next category, absorbable stents/biodegradable scaffolds at 15%. Similar differences were seen with only 14% of physicians excited about the possibilities for atherectomy and the same for drug eluting technology at 13%.
Technology physicians are most excited about the potential of in PAD. Surveyed in September 2025.
Intravascular Lithotripsy technology is rapidly transforming the treatment landscape for Peripheral Arterial Disease, with significant growth opportunities forecast. Tibial vessels are highlighted as the highest potential growth area for IVL technology as new, lower-profile devices with longer balloons enter the market.
IVL has revolutionised calcium management in vascular procedures. Physicians report IVL is dramatically reducing the need for stenting in femoral-popliteal treatments while improving safety profiles compared to traditional atherectomy.
‘IVL has transformed calcium management over the last few years,’ notes Kilian Toal, Director at medintel. ‘The ease of use, short learning curve, and applicability across most vessels mean it is rapidly becoming the first choice for many physicians in preparation for severe calcific disease.’
IVL is viewed by physicians as especially beneficial when treating diabetic and end-stage renal disease patients, populations projected to grow significantly in coming years.
While Shockwave Medical currently dominates the IVL market, competitive devices from companies including Bolt Medical (recently acquired by Boston Scientific), Abbott (through CSI acquisition), Amplitude Vascular Systems (AVS) and FastWave Medical are in development or early clinical trials.
Market competition is expected to intensify as reimbursement policies catch up with clinical practice and the growing evidence base continues to demonstrate IVL's effectiveness.
ENDS.
About the Research
Methodology Note: This analysis is based on a survey of 162 (US and EU interventional radiologists, vascular surgeons) conducted in September 2025. This survey represents a focused snapshot of early adopter perspectives rather than a comprehensive market study.
medintel is a specialist medical market research consultancy. For more information, contact intel@medintel.co.uk.
medintel has the capability to conduct larger-scale quantitative and qualitative research across broader physician populations. If you're interested in more extensive RDN market research or custom studies, please get in touch.
Renal Denervation Market Poised for Mainstream Adoption by 2030, New Physician Survey Reveals
New medintel survey: 75% of interventional cardiologists predict renal denervation will become standard hypertension treatment by 2030
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
75% of practicing interventional cardiologists predict procedure will become standard hypertension treatment despite current limited adoption
[October 31st 2025] - A new market research study by medintel reveals that renal denervation (RDN) is experiencing a remarkable resurgence, with three-quarters of interventional cardiologists practicing the procedure predicting the procedure will become mainstream hypertension treatment by 2030.
The survey of 123 interventional cardiologists across the United States and Europe found that while only 37% currently perform RDN procedures, 75% of those with hands-on experience believe the technology will achieve widespread adoption within five years.
"After nearly a decade in the wilderness following early clinical setbacks, renal denervation is back with rigorous evidence and renewed industry commitment," said Kilian Toal, Partner, at medintel. "The physician confidence we're seeing represents a fundamental shift in how the medical community views this technology."
Ends.
Background Notes:
Market Revival Built on Solid Foundation
The RDN market has transformed dramatically since its early boom-and-bust cycle. Initial enthusiasm in the 2010s led to major acquisitions, including Medtronic's $800 million purchase of Ardian. However, the field went quiet after Medtronic's pivotal Symplicity HTN-3 trial failed in 2014.
The current revival is anchored by FDA approvals in November 2023 for both ReCor Medical's Paradise ultrasound system and Medtronic's Symplicity Spyral radiofrequency system—the first renal denervation devices approved in the United States. Boston Scientific's recent $540 million acquisition of SoniVie signals renewed industry investment.
Technology and Patient Selection Trends Emerge
This research survey on renal denervation practices revealed clear preferences among practicing physicians:
80% prefer radiofrequency-based systems over ultrasound technology
68% identify resistant hypertension patients (on ≥3 medications) as the ideal candidates
US and European adoption rates are remarkably similar at 36% and 39% respectively
Barriers Remain But Solutions in Sight
Despite optimism, physicians identified key obstacles to broader adoption of renal denervation:
Access and reimbursement coverage (55% of respondents)
Patient identification and responder selection (52%)
Cost and hospital economics (48%)
Lack of long-term clinical evidence (43%)
Regional differences emerged, with US physicians more concerned about long-term evidence and economics, while European colleagues focused on patient selection and awareness.
Looking Ahead
The study suggests RDN's path to mainstream status depends on addressing systemic challenges around reimbursement, patient selection tools, and long-term evidence. A pending Medicare national coverage decision could serve as a pivotal catalyst for broader US adoption.
About the Research
Methodology Note: This analysis is based on a survey of 123 (US n=67 and EU n=56) interventional cardiologists conducted in August 2025. This survey represents a focused snapshot of early adopter perspectives rather than a comprehensive market study.
medintel is a specialist medical market research consultancy. For more information, contact intel@medintel.co.uk.
medintel has the capability to conduct larger-scale quantitative and qualitative research across broader physician populations. If you're interested in more extensive RDN market research or custom studies, please get in touch.
KOLs on Vascular Access Challenges in 2025
Leading EU and US vascular access specialists this month discussed critical developments in the field. The two hot topics were the withdrawal of endoAVF devices and the need for the development protocols on high-flow fistula management.
Leading EU and US vascular access specialists this month discussed critical developments in the field. Two topics of debate were the recent withdrawal of endoAVF devices and the need for the development protocols on high-flow fistula management.
Medtronic Withdraws Ellipsis EndoAVF Device
In a surprising development, Medtronic has withdrawn its Ellipsis endovascular arteriovenous fistula (endoAVF) device from the market. Despite positive clinical outcomes and strong patient preference due to cosmetic advantages and fewer complications, adoption challenges and cost barriers appear to have influenced this decision. Experts noted the device faced reimbursement hurdles in several markets despite commanding 85-90% of the global percutaneous fistula market. Despite the withdrawal, there is optimism about the future of endoAVFs with new technologies like the VENOS 2 study. The VENOS 2 study involves a new device that simplifies the procedure and shows early promise. Experts highlighted the need for a second-generation device to reduce the number of procedures required for fistula maturation.
High-Flow Fistulas Present Unaddressed Challenges
Experts interviewed identified high-flow fistulas as a significant yet under-recognised clinical challenge, particularly in post-transplant patients. With flows reaching two to three litres—effectively tripling cardiac output—these fistulas can cause considerable cardiovascular strain. Despite this, systematic follow-up and management algorithms remain lacking. Discussions emphasised the importance of monitoring and potentially intervening in high flow fistulas to prevent complications. Experts believed there is a need for more rigorous follow-up and research to develop strategies for managing high flow fistulas.
ENDS
Robotic Surgery After 30 Years Still Faces Adoption Challenges
Robotic surgery has been in use for approximately 20 years, initially gaining traction in urology, particularly for prostate cancer procedures. In 2005, the da Vinci surgical robot received FDA approval for gynecological applications, making gynecology the second specialty to adopt this technology. Since then, it has expanded to ENT, cardiothoracic, general, and colorectal surgery, with the latter specialties being more recent adopters.
Robotic surgery, now entering its third decade of clinical use, has revolutionised minimally invasive procedures across multiple specialties but medintel finds it still continues to face adoption hurdles.
Expanding Surgical Applications
Originally pioneered in urology, robotic platforms received FDA approval for gynecological applications in 2005. Applications have since expanded to ENT, cardiothoracic, general, and colorectal surgery. In gynecology, use has evolved from hysterectomies to pelvic floor repairs, myomectomies, and complex endometriosis cases.
‘Technology enhances skill, it does not replace it’
Robotic systems enhance surgical capabilities through improved precision, visibility, and ergonomics, but complement rather than replace expertise. Earlier complications stemmed primarily from inadequate surgical experience rather than technological limitations.
‘These platforms are sophisticated tools requiring proper training and sound surgical judgment’ explains a surgical director to medintel. ‘They enable minimally invasive approaches for complex cases but remain dependent on the surgeon's skill.’
Economic Realities Affect Implementation
Clinical evidence indicates robotic surgery can shorten hospital stays while reducing complications and readmission rates. However, realising these benefits requires sufficient platforms to serve surgical teams—a significant challenge in resource-constrained environments.
The pandemic has increased waiting times for non-urgent procedures, particularly in specialties like endometriosis surgery, driving more patients toward private care where robotics are more accessible.
Future Innovations
Recent advances include single-port systems for complex cases, though these await regulatory approval for gynecological applications. While AI is emerging in surgical training environments, autonomous robotic surgery remains distant due to the subjective nature of surgical decision-making.
The primary barrier to wider adoption remains economic, as more affordable systems with comparable quality are needed for full integration into healthcare systems worldwide.
ENDS
AI's Role In Research: Linear Connections Not Lateral
medintel continues to experiment with a range of AI platforms, and explore how AI can be used with phenomenal results while maintaining data privacy and safeguarding accuracy.
The massive boost to productivity, and speed of turnaround of immediate topline findings is a significant benefit as well as the ability to interrogate data to pursue lines of enquiry. However, the one-sided nature of the enquiry means it needs to be treated carefully. The lack of the ability for the researcher to see the whole picture in the data and see fresh perspectives can be a challenge. Researchers need to know the data to see the wider picture. In addition detailed storytelling still needs to be very much guided. AI serves as a powerful collaborative tool rather than a replacement for human expertise: for the time being anyway!
medintel continues to test the possibilities of the latest AI platforms, and utilise how AI with phenomenal analytical results while safeguarding data privacy and maintaining standards in accuracy and validity.
The massive boost to productivity, and speed of turnaround of immediate topline findings is a significant benefit as well as the ability to interrogate data to pursue lines of enquiry.
However, the one-sided nature of the enquiry means it needs to be treated carefully and can easily result in false positives.
The lack of the ability for the researcher to see the whole picture in the data and see fresh perspectives can be a challenge. Researchers need to know the data to see the wider picture. In addition detailed storytelling still needs to be very much guided. AI serves as a powerful collaborative tool rather than a replacement for human expertise: for the time being anyway!
AI as Research Assistant, Not Replacement
‘The most successful researchers view AI as an extension of their capabilities, not a substitute for their expertise,’ was noted on a recent forum of qualitative researchers.
AI Does Not Think Laterally: It Is Built On Linear Connections
AI is built on a series of yes, no, yes, no linear connections. It is not intuitively designed to think laterally. When humans think laterally, they make creative leaps between concepts, draw unexpected connections, and approach problems from unconventional angles. This often involves intuition, emotional context, and life experiences.
AI systems can simulate aspects of lateral thinking by making connections between seemingly unrelated concepts in training data; generate multiple approaches to solving problems and identify patterns across different domains.
However, AI lateral thinking doesn’t have genuine intuition or emotional context that often drives human creativity. AI connections are based on statistical patterns in training data rather than lived experience. As Claude AI describes:
‘I don't have the embodied understanding that humans develop through physical interaction with the world.’
Freeing Researchers for Higher-Value Work
This limitation aside, AI technology excels at handling repetitive tasks including transcript processing, pattern recognition, and response clustering. This efficiency creates more space for researchers to focus on deeper analysis and meaningful connections.
Recognising Critical Limitations
There are significant limitations in current AI capabilities, particularly regarding emotional intelligence and cultural context and the one directional nature of the enquiry. AI outputs accepted without critical evaluation, especially under deadline pressure are a concern.
Strategic Implementation Critical
The most effective AI integration occurs when technology is used as a reflective partner that helps identify bias and validate conclusions rather than generating independent insights. This approach creates what one participant called "an inexhaustible thought partner" that enhances rather than replaces human expertise.
A Collaborative Future
Like with most professions, AI is firmly part of the future of research, and as it evolves it may well lead to a shrinking workforce. AI certainly has the potential to mean greater volume of research done by fewer humans, but the human touch to guide the interrogation and pitch the narrative appropriate to the audience will likely remain.
ENDS
KOLs On PAD Innovations And Challenges In 2025
medintel interviewed leading vascular specialists to discuss advances in Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) treatments to understand key innovations. Following the successful LIFE BTK trial, bioresorbable scaffolds have emerged as potential game-changers for below-knee interventions.
medintel interviewed leading vascular specialists to discuss advances in Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) treatments to understand key innovations.
Bioresorbable Scaffolds Show Promise Below the Knee
Following the successful LIFE BTK trial, bioresorbable scaffolds have emerged as potential game-changers for below-knee interventions. This technology addresses both mechanical and biological factors affecting vessel patency. While experts expressed enthusiasm about devices like Abbott's Esprit™ BTK System scaffold, they cautioned about efficacy in longer lesions and suggested potential future applications beyond below-knee territories.
Limus-Based Therapies Gain Momentum
Development of sirolimus-coated balloons has accelerated, particularly for below-knee applications where paclitaxel devices have shown limited efficacy. The SIRONA trial demonstrated non-inferiority of sirolimus versus paclitaxel above the knee at one year. Specialists noted limus-coated devices show reduced distal embolization issues, though technical challenges in drug delivery remain.
Evidence Gap in Vessel Preparation Techniques
Despite widespread use of vessel preparation methods including specialty balloons, lithotripsy, and atherectomy, experts highlighted the lack of robust evidence demonstrating improved outcomes. High-cost devices require stronger proof of clinical benefit, with successful strategies likely needing combination with definitive treatments rather than functioning independently.
ENDS
Challenges of Ethnographic Research on Continuous Glucose Monitoring
A recent ethnographic project on Continuous Glucose Monitoring use among Type 1 Diabetes Patients in the US and Germany made use reflect on the following project management issues…
A recent ethnographic project on Continuous Glucose Monitoring use among Type 1 Diabetes Patients in the US and Germany made use reflect on the following project management issues:
Recruitment and Selection Barriers
Finding representative participants for ethnographic research on continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices presented significant challenges in a recent study in US and Germany. In the US, the fragmented healthcare system creates access disparities, making it difficult to recruit across socioeconomic boundaries. Many lower-income patients lack access to advanced CGM technologies, potentially biasing research toward more affluent participants. In Germany, despite universal healthcare, we found recruitment often requires navigating multiple clinical gatekeepers and regional health authorities, extending timelines and adding administrative complexity.
Cultural Differences in Health Technology Perception
American and German patients approach health technology differently, complicating comparative analysis. US patients often view CGMs through a consumer technology lens, focusing on features and convenience. German patients typically prioritize precision, reliability, and data privacy, reflecting broader cultural attitudes toward healthcare and technology. These differences influence how patients interact with devices and their willingness to share experiences, requiring researchers to adapt their methodological approaches for each context.
Data Privacy and Regulatory Compliance
Germany's strict data protection laws under GDPR created additional hurdles for collecting observational data about CGM use in natural settings. Requirements around explicit consent for each data collection point posed a challenge for ethnographic work. The US presents different challenges with HIPAA compliance and varied state-level privacy regulations, particularly when research crosses insurance and provider boundaries.
Technology Ecosystem Variations
The surrounding technology ecosystem significantly impacts CGM usage patterns. US patients typically use a wider range of connected apps and digital platforms to manage their diabetes, while German users often rely more heavily on their primary healthcare provider's recommended systems. We had to account for these different ecosystems when analysing how patients integrate CGMs into their daily diabetes management routines.
Longitudinal Engagement Challenges
Maintaining consistent participation proved a challenge both countries. In the US, high patient mobility and insurance changes caused challenges. German participants may exhibit greater stability but often show more reluctance toward continuous remote monitoring aspects of research, particularly when it involves sharing data outside their immediate healthcare environment.
Market Engagement Model
Our engagement approaches are tailored to each client's unique needs, ranging from value-proposition workshops to executive education, team coaching, and project consulting.
Introduction
Our engagement approaches are tailored to each client's unique needs, ranging from value-proposition workshops to executive education, team coaching, and project consulting.
Below is our structured seven-phase model that guides successful market engagements.
Phase 1: Situation Analysis
This initial phase evaluates current market positioning, identifying existing value propositions and delivery systems. We assess how effectively these deliver value to customers and shareholders, and examine vulnerabilities against market trends and disruptions.
Phase 2: Common Language and Customer Mindset
We establish a shared customer-centric framework for your team. This provides essential tools to understand customer needs while building organisational buy-in for the reinvention process.
Phase 3: Research Preparation
We synthesize current knowledge about unmet customer needs in target segments. Role-playing exercises help formulate initial hypotheses about promising opportunities, preparing teams for field research.
Phase 4: Customer Field Research
We study actual customers whose lives we aim to improve, identifying problems they may not recognize themselves. This typically involves 10-15 in-depth interviews per market opportunity, professionally facilitated to capture maximum insights.
Phase 5: Value Architecture
Using research insights, we develop improved customer scenarios with superior value propositions and delivery systems. These define the ideal future state that solves customer problems in innovative ways, specifying experiences and price points that motivate customers to choose your solutions.
Phase 6: Concept Testing
We create narrative descriptions of new scenarios to test with customers. Team members revisit selected customers to validate these concepts, confirming their potential success or identifying necessary revisions.
Phase 7: Finalization and Launch
We evaluate, refine, and implement the most promising value propositions. This includes developing business cases and estimating market potential.
Maximising Impact Through Strategic Market Research
In today's competitive healthcare landscape, the difference between products is increasingly marginal, making effective research essential before product introduction. Well-designed research ensures new healthcare products are not only clinically efficacious but also effective and acceptable in real-world settings. Understanding end-users and the healthcare-commercial ecosystem is crucial for maximizing impact and return on investment across all development stages.
The Critical Role of Research in Healthcare Innovation
In today's competitive healthcare landscape, the difference between products is increasingly marginal, making effective research essential before product introduction. Well-designed research ensures new healthcare products are not only clinically efficacious but also effective and acceptable in real-world settings. Understanding end-users and the healthcare-commercial ecosystem is crucial for maximizing impact and return on investment across all development stages.
Integrating Research Throughout the Product Lifecycle
Social and behavioral research should operate alongside product development as a critical component of the process. These techniques help answer market-critical questions about current behaviors, unmet needs, evaluation criteria, system challenges, and innovation opportunities. Appropriate research supports decision-making at all lifecycle stages—from early concept development through launch and post-market monitoring—significantly reducing risk at decision-making milestones.
Key Research Approaches for Different Development Phases
Different research methodologies serve specific phases of product development. Early-stage research focuses on needs assessment and concept testing. Mid-stage development benefits from product refinement studies and human-centered design approaches. Launch-phase research emphasizes message testing and market forecasting, while post-launch efforts concentrate on tracking studies and further refinement opportunities.
Essential Market Research Principles
Six critical principles emerge from successful market research: (1) Innovation should be continuous rather than seeing products as "finished"; (2) Comprehensive market understanding requires including all stakeholders and avoiding assumptions; (3) Testing should examine context and ideas surrounding the product, not just the product itself; (4) Research should strengthen products, not merely evaluate them; (5) Rigorous forecasting is essential for appropriate planning; (6) Ongoing tracking sustains success even after launch.
Effective Implementation Strategies
For maximum benefit, research should be incorporated from the earliest stages—even before concept development. Professional research partners help ensure appropriate design and execution. The actionability of findings depends on employing correct methodologies and ensuring outcomes inform organizational planning. This approach optimizes public health interventions by developing strong understanding of all relevant stakeholders from end-users to product developers, commercial groups, and government entities.
Qualitative Research Techniques: Understanding Patient Quality of Life
We recently completed an in-depth study with diabetes patients, and wanted to reflect on some of the projective techniques the team used to elicit information.
We recently completed an in-depth study with diabetes patients, and wanted to reflect on some of the projective techniques the team used to elicit information.
Visual Exploration Methods
Image-Based Expression: We asked diabetes patients to create collages representing their daily experiences with the condition. This helped us uncover emotional dimensions that standard questionnaires might miss. When patients selected images showing isolation during mealtimes or anxiety in social settings, they revealed quality of life challenges they hadn't articulated in direct questioning. Their explanations of these visual choices provided rich insights into lived experiences.
Archetype Analysis: Presenting Archetypes to patients revealed how they viewed themselves at different stages of their diabetes journey. This technique helped us understand the psychological evolution from diagnosis through adaptation. Many initially identified with a Victim archetype but transitioned to Hero or Caregiver as they mastered self-management.
Disease Experience Personification
Character Development: Having patients describe diabetes as a person in their lives uncovered profound emotional relationships with the condition. This metaphorical approach helped us identify that many long-term patients personified their diabetes as an "unwelcome roommate" they had learned to accommodate rather than a "mortal enemy" to be fought.
Contextual Scenarios: Scenario exercises like "hosting a dinner party while managing diabetes" illuminated social challenges that significantly impacted quality of life. These discussions helped us identify previously unrecognized barriers to treatment adherence in social contexts.
Interactive Exploration
Recognition Activities: Device and medication identification exercises sparked productive discussions about treatment experiences. This approach helped us understand how physical interactions with management tools affected emotional wellbeing and treatment satisfaction.
Classification Exercises: Having patients sort aspects of diabetes management into categories revealed that continuous glucose monitoring caused less life disruption than previously assumed, while dietary restrictions created more significant quality of life burdens than clinicians typically recognized.
Narrative Techniques
Creative Writing: Patient-written letters to newly diagnosed individuals helped us identify emotional milestones in the adaptation process that healthcare providers often overlooked when developing support programs.
Situational Storytelling: Patient narratives about navigating healthcare systems uncovered systematic barriers to optimal care that directly impacted quality of life, particularly around appointment scheduling and medication access.
Supplementary Methods
Association Mapping: Placing care elements in concentric circles helped us visualize which aspects of diabetes management created the greatest burden, revealing that administrative tasks often caused more distress than medical procedures.
These techniques provided deeper insights into diabetes patients' lived experiences beyond clinical measures, fundamentally reshaping our understanding of quality of life factors in diabetes management.